Rubber Process Analyzer
The EKT-2003RPA Rubber Process Analyzer is a newest technology rubber-testing and testing equipments instrument, which measuring the Viscosity and Elastic of Polymer properties by dynamic mechanical testing system.
Our dynamic rheometer is designed with rotorless (Moving Die) cavity structure and provides dynamic, strain, modulus measurements in different temperature condition. Using this instrument can create not only better product quality it’s also very suitable for laboratory institution of detail research & development of Rubber Compound.
Special Features and Functions
- Quick Temperature Heat-Up and stabilization
- Greater sensitivity and precision torque measuring system
- Multiple Test Functions
- Simplify Operation
- SPC Statistics Software
|
|
|
|
Frequency |
0.01 to 50Hz (0.6 to 3,000 cpm) |
|
Strain |
±0.7%~±1256% (±0.05 to ±90 degrees) |
|
Torque |
0.01~200 lbf-in ( 0.01~226 dN-m) |
|
Temperature |
Ambient+5 to 230 °C (resolution 0.1 °C) |
|
Maximum Ramp Rate |
1 ℃/s |
|
Maximum Cool Rate |
0.5 ℃/s |
|
Measured Data |
Torque, temperature, frequency, strain |
|
Calculated Data |
G’, G”, G*, J’, J”, J*, S*, S”, tanδ,η’, η”, η* |
|
Applicable Standards |
ASTM D5289, D6084, D6204, D6601, D7050 |
Sequential, reliable, and unattended measurements are made using an automation sample feed system. And the automation system is divided in to two types: linear automation and tray automation.
Linear automation
---5pcs sample loading

KT-2003RPA-S
Tray automation
---50pcs or 60pcs sample loading

EKT-2003RPA-AUTO
According to test variable, the most commonly used applications as described below.
- Strain: a strain sweep can be used to investigate the Payne effect and also to understand Large Amplitude Oscillatory Shear (LOAS) effects at high strain rates.
(a) Payne Effect
A feature of the
stress–strain behavior of rubber, especially rubber compounds containing
fillers such as carbon black.
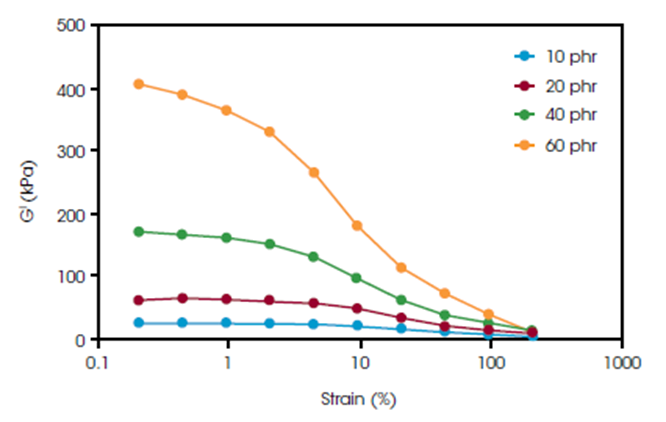
The impact of carbon block addition at five different levels is seen in the low strain region. High strain behavior is general insensitive to filler addition, as it is less sensitive to filler interaction.
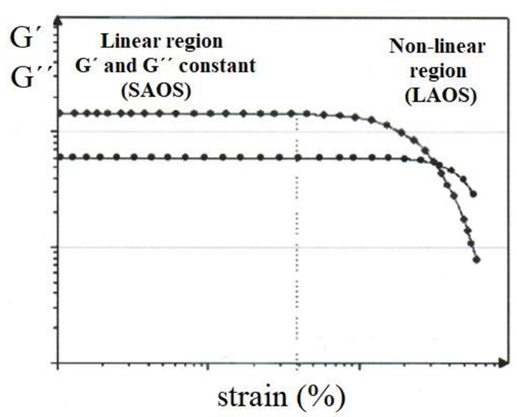
(b) Large Amplitude Oscillatory Shear (LOAS) effects
The large amplitude oscillatory shear testing (LAOS) is a commonly used method to characterizing the branching structure.
-
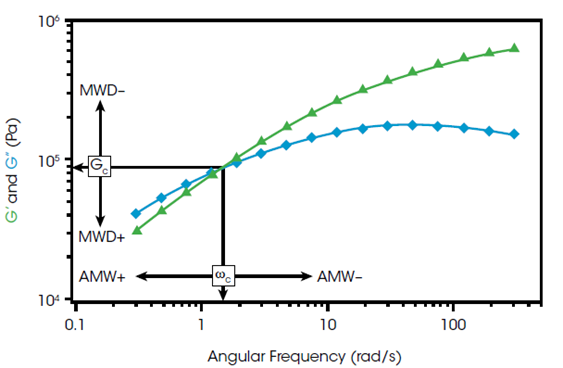
Frequency: testing at frequencies can be used to characterize
the frequency-dependent material response, most often in terms of the
elastic and viscous components. Frequency sweep as shown can reveal information about the average molecular weight
(crossover frequency) and molecular weight
distribution (crossover modulus).
- Temperature: using an RPA, temperature control can either be constant (isothermal) or variable (non-isothermal). An isothermal test can be used to measure the cure properties of raw rubber. Non-isothermal testing can be used to explore more complicated curing characteristics or understand the processability of a raw polymer.
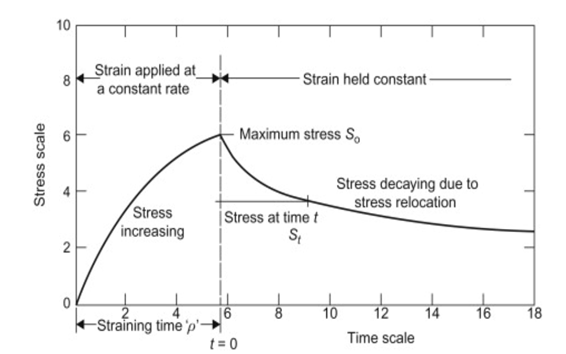
-
Time: accounting
for time is a key consideration when assessing the processability of a raw
material. A Stress Relaxation test is a defined test method for measuring
the decay in stress over time as a material is allowed to relax.